|Loan_ID | Gender| Married |Dependents|Education |Self_Employed|ApplicantIncome|
|----|---|----|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|LP001002 | Male | No | 0 | Graduate | No | 5849 |
| LP001003 | Male | Yes | 1 | Graduate | No |4583 |
| LP001005 | Male | Yes | 0 | Graduate | Yes | 3000|
| LP001006 | Male | Yes | 0 |Not Graduate | No | 2583|
|LP001008| Male | No| 0 | Graduate| No | 6000|
|CoapplicantIncome| LoanAmount | Loan_Amount_Term |Credit_History |Property_Area| Loan_Status |
|---|---|
| 0.0 | NaN | 360.0 | 1.0 | Urban | Y |
| 1508.0| 128.0| 360.0| 1.0 | Rural | N |
| 0.0 |66.0| 360.0| 1.0 | Urban | Y |
| 2358.0| 120.0| 360.0| 1.0 | Urban | Y |
| 0.0 | 141.0| 360.0| 1.0 | Urban | Y |
Dataframe named "df5"
Q:1)数据处理(类型区分)

因为DataFrame里混合着类别特征列和连续数据特征列,每一个数据科学家需要知道怎么区别处理它们。那么如何计算列表里类别特征列的数量?
A (df5.dtype == 'object').sum()
B (df5.dtypes == object).sum()
C (df5.dtypes == object).count()
运行结果:
A
'DataFrame' object has no attribute 'dtype'
B
8
C
13
答案:B
解读:
当df中既有连续数据又有类别时,所有数据的类别被改为“object”
每一列都有自己的dtype, df5.dtypes == object就是判断每一列的类型是否是object,
sum()计算所有是object的列的数量
初看,其实只发现有7列是object,但是我们打印出来看
print df5_test.dtypes
Loan_ID object
Gender object
Married object
Dependents object
Education object
Self_Employed object
ApplicantIncome int64
CoapplicantIncome float64
LoanAmount float64
Loan_Amount_Term float64
Credit_History float64
Property_Area object
Loan_Status object
发现Dependents是object,再看df5中该列都是数字,那么再去查原数据文件
因为我取的是前5行,在第9行出现了3+。
那么可以推测在读取CSV文件时,每一列的类型就确定了,不会因取的前几行而改变。
count()返回的是非null列的数量,在这里就是所有列的数量了
经过实验,即使有一列的值全是NaN,count仍然会把这一列当成非null列。
Q:2) 数据处理(统计类别)

找出在“Property_Area”类别列里的所有的类别
A df5.Property_Area.indiviuals()
B df5.Property_Area.distinct()
C df5.Property_Area.unique()
运行结果:
A
'Series' object has no attribute 'indiviuals'
B
'Series' object has no attribute 'distinct'
C
['Urban' 'Rural']
答案:C
解读:
经过搜索panda文档,文档中没有indiviuals()和distinct(),而unique的返回值是一个矩阵,可以索引。
Q:3) 缺失值(寻找)

有的列中会缺少值,那么请找出“LoanAmount”列中有多少缺失值?
A df5.count().maximum()-df5.LoanAmount.count()
B (df5.LoanAmount == NaN).sum()
C (df5.isnull().sum()).LoanAmount
运行结果:
A
'Series' object has no attribute 'maximum'
B
name 'NaN' is not defined
C
1
答案:C
解读:
将A选项中,maximum()修改为max(),就对了,DataFrame的count()是计算每一列的非Nan数,返回的是个serial.
Loan_ID 5
Gender 5
Married 5
Dependents 5
Education 5
Self_Employed 5
ApplicantIncome 5
CoapplicantIncome 5
LoanAmount 4
Loan_Amount_Term 5
Credit_History 5
Property_Area 5
Loan_Status 5
serial的count()是计算该列的非NaN数,但是不建议这么计算缺失值个数,还是用选项C这种直接的方式更可靠
在B选项中,可以看出NaN不能按照数值来使用。
在C选项中,df5.isnull()返回的是一个Dataframe:
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed ApplicantIncome \
0 False False False False False False False
1 False False False False False False False
2 False False False False False False False
3 False False False False False False False
4 False False False False False False False
CoapplicantIncome LoanAmount Loan_Amount_Term Credit_History Property_Area \
0 False True False False False
1 False False False False False
2 False False False False False
3 False False False False False
4 False False False False False
然后sum()得到每一列的和,返回一个serial:
Loan_ID 0
Gender 0
Married 0
Dependents 0
Education 0
Self_Employed 0
ApplicantIncome 0
CoapplicantIncome 0
LoanAmount 1
Loan_Amount_Term 0
Credit_History 0
Property_Area 0
Loan_Status 0
所以.LoanAmount就得到该索引的指。想对而言,还是C选项比较好,不容易出错。
Q:4)处理缺失值-方法一(删除所在行)

在Dataframe中的一些列里(“LoanAmount”)有缺失的值,如何把有缺失值的那一行去掉?
A new_dataframe = df5[~df5.LoanAmount.isnull()]
B new_dataframe = df5[df5.LoanAmount.isna()]
C new_dataframe = df5[df5.LoanAmount.is_na()]
运行结果:
A
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed \
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 Graduate No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 Graduate Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 Not Graduate No
4 LP001008 Male No 0 Graduate No
B
'Series' object has no attribute 'isna'
C
'Series' object has no attribute 'is_na'
答案:A
解读:
isnull()将列表的对应位置变成布尔值,然后取反
0 False
1 True
2 True
3 True
4 True
但是放到df5[]中,就能滤掉false那一行,这是Dataframe的bool值索引的使用。
Q:5)处理缺失值-方法二(删除缺失n个值以上的行)

在DataFrame里,有一些行中,缺失了大量信息,那么就需要移除这些行。那么假设我们规定只要是缺失了超过0个值的行,即只要有一个缺失值就删除(因为我们的数据里只有一行缺失了一个值),就要移除。那么怎么做到呢?
A temp = df5.dropna(axis = 0, how = 'any', thresh = 0)
B temp = df5.dropna(axis = 0, how = 'all', thresh = 0)
C temp = df5.dropna(axis = 0, how = 'any', thresh = df5.shape 1 - 0)
运行结果:
A
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed \
0 LP001002 Male No 0 Graduate No
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 Graduate No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 Graduate Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 Not Graduate No
4 LP001008 Male No 0 Graduate No
B
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed \
0 LP001002 Male No 0 Graduate No
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 Graduate No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 Graduate Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 Not Graduate No
4 LP001008 Male No 0 Graduate No
C
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed \
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 Graduate No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 Graduate Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 Not Graduate No
4 LP001008 Male No 0 Graduate No
答案:C
解读:
dropna()函数,axis = 0 :行,axis = 1 :列;
how = 'any' :该行或该列至少有thresh个非NaN时,将其保留
how = 'all' :仅在该行或该列全为NaN时,才抛弃该行(列)
df5.shape返回一个列表,说明DataFrame的维度,结果如下。
(5, 13)
df5.shape[1]即列数,thresh = df5.shape[1] - 0 = 13 ,即至少有13个非NaN的行,才会被保留。
Q:6)数据处理(类别合并)

在整理数据的时候,你会发现在'Property_Area'这一列里,是Rural的行很少(原文里是Semiurban,但是我这里的数据没有Semiurban),那么经过分析,可以把Rural和Urban合并成新类别City(这里不太合理,但是学会技术就好了),怎么操作呢?
A turn_dict = ['Urban' : 'City', 'Rural' : 'City']
df5.loc[ : , 'Property_Area'] = df5.Property_Area . replace(turn_dict)
B turn_dict = {'Urban' : 'City', 'Rural' : 'City'}
df5.loc[ : , 'Property_Area'] = df5.Property_Area . replace(turn_dict)
C turn_dict = {'Urban' : 'City', 'Rural' : 'City'}
df5.loc[ : , 'Property_Area'] = df5.Property_Area . update(turn_dict)
运行结果:
A
invalid syntax
B
Credit_History Property_Area Loan_Status
0 1.0 City Y
1 1.0 City N
2 1.0 City Y
3 1.0 City Y
4 1.0 City Y
C
'dict' object has no attribute 'reindex_like'
答案:B
解读
print df5.Property_Area
0 Urban
1 Rural
2 Urban
3 Urban
4 Urban
所以df5.Property_Area是个serial, 而serial.update()的参数只能是serial,将serial完全替换
turn_serial = pd.Series(['1','2','City','City','City'])
print df5.Property_Area.update(turn_serial)
0 1
1 2
2 City
3 City
4 City
print df5
Credit_History Property_Area Loan_Status
0 1.0 1 Y
1 1.0 2 N
2 1.0 City Y
3 1.0 City Y
4 1.0 City Y
而serial.replace()的参数可以是dict,与update()相比,可以选则一部分替换,但是还需要赋值到df5.loc[]里,否则是无效的,如下:
turn_dict = {'Urban' : 'City'}
print df5.Property_Area.replace(turn_dict)
0 City
1 Rural
2 City
3 City
4 City
print df5
Credit_History Property_Area Loan_Status
0 1.0 Urban Y
1 1.0 Rural N
2 1.0 Urban Y
3 1.0 Urban Y
4 1.0 Urban Y
df5.loc[ : ,'Property_Area'] = df5.Property_Area.replace(turn_dict)
print df5
Credit_History Property_Area Loan_Status
0 1.0 City Y
1 1.0 Rural N
2 1.0 City Y
3 1.0 City Y
4 1.0 City Y
Q:7)数据分析(多条件统计)

在看这些数据的时候,你会发现女性结婚的人的比例好像比较高,那么计算一下真实的比例。
A (df5.loc[(df5.Gender == 'male') && (df5.Married == 'yes')].shape 1 / float(df5.shape[0])) * 100
B (df5.loc[(df5.Gender == 'Male') & (df5.Married == 'Yes')].shape 1 / float(df5.shape[0])) * 100
C (df5.loc[(df5.Gender == 'male') and (df5.Married == 'yes')].shape[ 0 ] / float(df5.shape[0])) * 100
D None of these
运行结果:
A
invalid syntax
B
260
C
The truth value of a Series is ambiguous.
答案:D
解读:
loc[]函数用标签来索引,loc[ : , : ] 逗号前是行索引,逗号后是列索引。
print df5.loc['1':'3','Gender':'Dependents']
Gender Married Dependents
1 Male Yes 1
2 Male Yes 0
3 Male Yes 0
若是只有一个参数,则是索引行(row)的,因为单参数索引列(column)是用df5['Gender']。
print df5.loc['1':'3']
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed ....
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 Graduate No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 Graduate Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 Not Graduate No
loc[]里也可以放bool值的列表
print df5.loc[[False,True,True,True,False],'Gender']
1 Male
2 Male
3 Male
而df5.Gender == 'Male') & (df5.Married == 'Yes')得到的是个bool值列表
print (df5.Gender == 'Male') & (df5.Married == 'Yes')
0 False
1 True
2 True
3 True
4 False
print df5.loc[(df5.Gender == 'Male') & (df5.Married == 'Yes')]
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed ....
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 Graduate No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 Graduate Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 Not Graduate No
所以正确的表达是
print (df5.loc[(df5.Gender == 'Male') & (df5.Married == 'Yes')].shape[0] / float(df5.shape[0])) * 100
60.0
Q:8)数据处理(训练数据和测试数据的columns不一致)

如果你发现,给你提供的训练数据和测试数据的columns不一致,怎么找出那些在测试数据中,不在训练数据中的column? 测试数据的clomns如下:
|Loan_ID | Gender| Married |Dependents|Education |Self_Employed|Age|
|--|
A set( test .columns ) .difference( set( df5 .columns ) )
B set( test .columns .tolist() ) - set(df5. columns. tolist())
C set(df5 .columns .tolist() ). difference(set(test. columns. tolist() ) )
D Both A and B
运行结果:
A
set(['Age'])
B
set(['Age'])
C
set(['Property_Area', 'CoapplicantIncome', 'LoanAmount', 'ApplicantIncome', 'Loan_Amount_Term', 'Loan_Status', 'Credit_History'])
答案:D
解读
set()是建立一个无序不重复集合,set(a).difference(set(b))-->返回一个新的 set 包含 a 中有但是 b 中没有的元素
index.tolist()返回一个index值组成的列表
print df5.columns
Index([u'Loan_ID', u'Gender', u'Married', u'Dependents', u'Education',
u'Self_Employed', u'ApplicantIncome', u'CoapplicantIncome',
u'LoanAmount', u'Loan_Amount_Term', u'Credit_History', u'Property_Area',
u'Loan_Status'],
dtype='object')
print df5.columns.tolist
['Loan_ID', 'Gender', 'Married', 'Dependents', 'Education', 'Self_Employed', 'ApplicantIncome', 'CoapplicantIncome', 'LoanAmount', 'Loan_Amount_Term', 'Credit_History', 'Property_Area', 'Loan_Status']
set(a)-set(b)-->跟difference的作用一样。
C选项错的原因是得到的是df5里有,test里没有的,恰恰相反。
Q:9)数据处理(类型变量转换为数值型变量)

有时候我们需要把类别类型列表下的各种类型数值化,方便算法使用数据。例如,如何把'Education'列表下的Graduate-->1、Not Graduate-->0 ?
A - df5.ix[:, 'Education'] = df5.Education.applymap({'Graduate':1,'Not Graduate':0}).astype(int)
B - df5.ix[:, 'Education'] = df5.Education.map({'Graduate':1,'Not Graduate':0}).astype(int)
C - df5.ix[:, 'Education'] = df5.Education.apply({'Graduate':1,'Not Graduate':0}).astype(int)
看到这道题的时候,是不是有点熟悉,再回过头看看第6题,我们先试试用第6题的方法,能不能解决这个问题。
turn_dict = {'Graduate':1,'Not Graduate':0}
df5.loc[:,'Education'] = df5.Education.replace(turn_dict)
print df5
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed \
0 LP001002 Male No 0 1 No
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 1 No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 1 Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 0 No
4 LP001008 Male No 0 1 No
可以看出,完全正确。我们再来看这道题的方法。
运行结果:
A
'Series' object has no attribute 'applymap'
B
Loan_ID Gender Married Dependents Education Self_Employed \
0 LP001002 Male No 0 1 No
1 LP001003 Male Yes 1 1 No
2 LP001005 Male Yes 0 1 Yes
3 LP001006 Male Yes 0 0 No
4 LP001008 Male No 0 1 No
C
'dict' object is not callable
答案:B
解读
df5.ix[:,:]与df5.loc[:,:]的区别在于,ix[]可以用数字和lable混合索引,而loc[]只能用lable索引
a.map(b)将b的指给a ,b可以是serial,也可以是dict,感觉跟replace差不多。
.astype(int)强制将该serial的数据类型转换为int
Q:10)数据处理(训练数据、测试数据的'类别列' 数据存在差异)
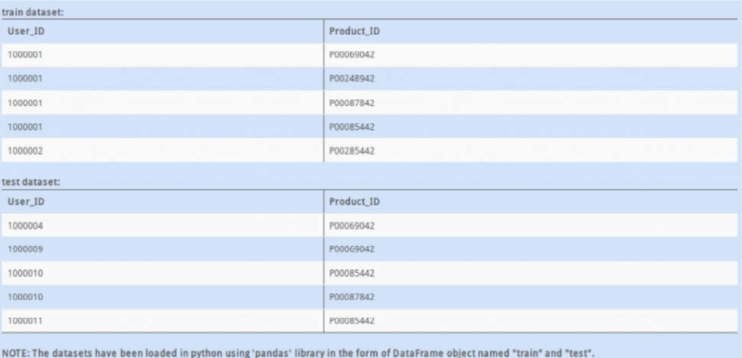
如图,上方是训练数据,下方是测试数据。
它们 Product_ID 列的数据并不是在同一个集合,那么,在测试时有的 Product_ID 没有历史数据,就会带来麻烦。
问题:
如何确定test里的`Product_ID`都有历史数据,即是否在train里都出现过?
因为没有原始数据,只取图片里的前三行建成DataFrame
train_dict = {'User_ID':['1000001','1000001','1000002'],
'Product_ID':['P00069042','P00248942','P00087842']
}
train = pd.DataFrame(train_dict,columns=['User_ID','Product_ID'])
test_dict = {'User_ID':['1000004','1000009','1000010'],
'Product_ID':['P00069042','P00085442','P00087842']
}
test = pd.DataFrame(test_dict,columns=['User_ID','Product_ID'])
print train
User_ID Product_ID
0 1000001 P00069042
1 1000001 P00248942
2 1000002 P00087842
print test
User_ID Product_ID
0 1000004 P00069042
1 1000009 P00085442
2 1000010 P00087842
A - train.Product_ID.unique().contains(test.Product_ID.unique())
B - set(test.Product_ID.unique()).issubset(set(train.Product_ID.unique()))
C - train.Product_ID.unique() = test.Product_ID.unique()
答案
B
(1)分析
column.unique() : 得到这个column 的所有种类,返回数组
print train.Product_ID.unique()
['P00069042' 'P00248942' 'P00087842']
set():建立无序不重复集合
s.issubset(t) : s <= t # 测试是否 s 中的每一个元素都在 t 中
其实,这道题无须使用unique(),因为set()直接可以生成一个无序不重复的集合。
(2)运行结果
A
AttributeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object has no attribute 'contains'
B
False
C
SyntaxError: invalid syntax